Learning the general facts about cannabis is important and extremely helpful when visiting a dispensary. If it happens to be your first time, then you are in good hands because our budtenders at 253 will be able to assist you in finding what may be the best for you in what you are looking for. As is, it is important to know that everyone experiences cannabis in their own way depending on the method used, the dose, and the variety of the product.
Strain Varieties:
There are three strain varieties known as sativa, hybrid, and indica, and these are used as shorthand for the general range of effects that various strains can produce. Sativas tend to provide more energizing effects that pair well with physical activity and creative projects, suggesting they are more suited for daytime use. In contrast, Indica strains are believed to be physically sedating, causing tiredness or unclear thinking, which is why they are generally best for evening. Most strains you will encounter are in fact hybrids that can be characterized as either sativa-dominant or indica-dominant.
It is important to remember the effect that cannabis has on you, because it is much more personal. The product’s chemical profile (its cannabinoids and terpenes), your unique biology and tolerance, the dose, and the consumption method all play a part in your own resulting experience. Learning about strain varieties, as well as how different cannabinoid and terpene profiles can affect you will help you when finding the right fit for your particular needs.
Indica’s are likely to…
- Relax muscles
- Reduce spasms, pain, and inflammation
- Promote sleep
- Reduce anxiety
- Relieve nausea
- Stimulate appetite
- Reduce pressure in the eyes
Sativa’s are likely to…
- Elevate mood
- Increase energy
- Increase focus
- Promote creativity
- Stimulate appetite
Cannabinoids – [ kuh–nab–uh-noids ]
Cannabinoids are the naturally occurring active compounds found in the cannabis plant. These chemical compounds secreted by the cannabis flowers interact with our bodies to provide relief to an array of symptoms some including pain, anxiety, nausea, or inflammation.
Most cannabinoids will not get you high. In fact, THC is the only plant cannabinoid that has clear intoxicating effects on its own. And THC actually doesn’t occur naturally in the raw flower. Instead, it produces the non-psychoactive THC-A which must be “activated” (decarboxylated), by heat or vaportization, to yield THC.
While most plant cannabinoids are not intoxicating themselves, their presence can influence how THC affects you. The best example of this comes from CBD. Even though it wouldn’t get you high by itself, it influences the way that THC interacts with the CB1 receptors in your endocannabinoid system, and can therefore influence exactly how a cannabis product will affect you.
At 253, we place specific labels on our cannabis products that will breakdown the cannabinoid profile for you so that you can see the ratio of the compounds that are present. This can help you understand the potential therapeutic and psychoactive effects or each product. Check out our dictionary below.
Cannabinoid Dictionary
THC – Tetrahydrocannabinol (ˈte-trə-ˌhī-drə-kə-ˈna-bə-ˌnȯl)
Cannabis’ psychoactive effects are primarily attributed to THC, which is also particularly effective in relieving nausea, appetite loss, insomnia, among other symptoms.
THC-A – Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (te-trə-ˌhī-drə-kə-ˈna-bə-ˌnȯl-ik ˈa-səd)
THCA is the primary non-psychoactive compound in cannabis, from which THC is derived through activation by heat or other extraction methods. If this compound is used in its natural state, then one can benefit from its ability to reduce pain, inflammation and anxiety without the high.
THCV – Tetrahydrocannabivarin (te-trə hī-drə-kə-ˈna-bə-ver-in)
THCV is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid that interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, among other targets in the body. It is typically found in cannabis only in trace amounts and its effects in humans are still being highly researched today. Researchers claim it is known to be an appetite suppressant and help with diabetes, as well as reducing panic attacks, helping with Alzheimers, and stimulates bone growth.
CBD – Cannabidiol (kan-ə-bə-ˈdī-ˌȯl)
CBD is non-psychoactive (does not induce a euphoric high) with a calming effect helpful for those treating anxiety and sleep loss. CBD has also been shown to lower blood sugar and treat pain, multiple sclerosis, inflammation, stress disorders, and epilepsy.
CBDA – Cannabidiolic Acid (kanə-bə-dälˈik asəd)
CBDA is a common, non-intoxicating cannabinoid in cannabis and is the predecessor of CBD, which can be found in trichomes on raw and uncured cannabis. Through a process called decarboxylation, CBDA converts to CBD. In one study, researches noticed CBDA affecting levels of Serotonin within the body, which is vital to core human functions like motor skills, sleeping, eating, digestion, and emotions.
CBC – Cannabichromene (kanə-bə-krō’mēn)
CBC is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid with known robust anti-inflammatory properties. CBC binds to the body’s TRPA1 receptor, which is a lesser-known component of the endogenous cannabinoid system. Research suggests that CBC has cancer fighting potential because of how it reacts with the body’s natural endocannabinoid called anandamide. CBC has been shown to block pain and inflammation associated with collagen-induced osteoarthritis, and provide a lot of antidepressant properties.
CBGA – Cannabigerolic Acid (kanə-bə-ge-ralˈik asəd)
CBGA is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid that is the precursor for THC, CBD, and several other common cannabinoids. Enzymes known as synthases are responsible for converting CBGA into molecules such as THCA. Research and studies suggest that CBGA contains antitumor properties.
CBL – Cannabicyclol (kanə-bīsək -lōl)
CBL is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant, and the compound forms when CBC is exposed to environmental changes. CBL is regularly found in many varieties of cannabis, but research has yet to determine how it interacts with receptors in the human body.
CBLA – Cannabicyclolic Acid (kanə-bīsək -lōlik asəd)
CBLA is a rare, non-intoxicating compound that originates from CBCA then converts to CBLA when it is exposed to natural environmental changes during storage. CBLA has been studied for its anti-inflammatory properties, among other potential benefits.
CBN – Cannabinol (kan-ə-bī-nȯl)
CBN is s a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid found only in trace amounts in Cannabis, and is degraded product of THCA. CBN is the cannabinoid into which THC breaks down after prolonged periods of time. The degradation can be accelerated by exposing dried plant matter to oxygen and heat. Research claims it is ¼ the potency of THC.
CBDV – Cannabidivarin (kuh-nab-di-var- ən)
CBDV is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant that is similar to CBD. CBDV interacts with components of the endocannabinoid system to regulate brain function, and it shows strong promise in the treatment of epilepsy.
1:1 – THC/CBD Hybrid
One-to-one products combine the benefits of each compound while tempering the psychoactive effects of a typical THC product. Many people find this useful if they don’t want a strong high while retaining the therapeutic benefits of both.
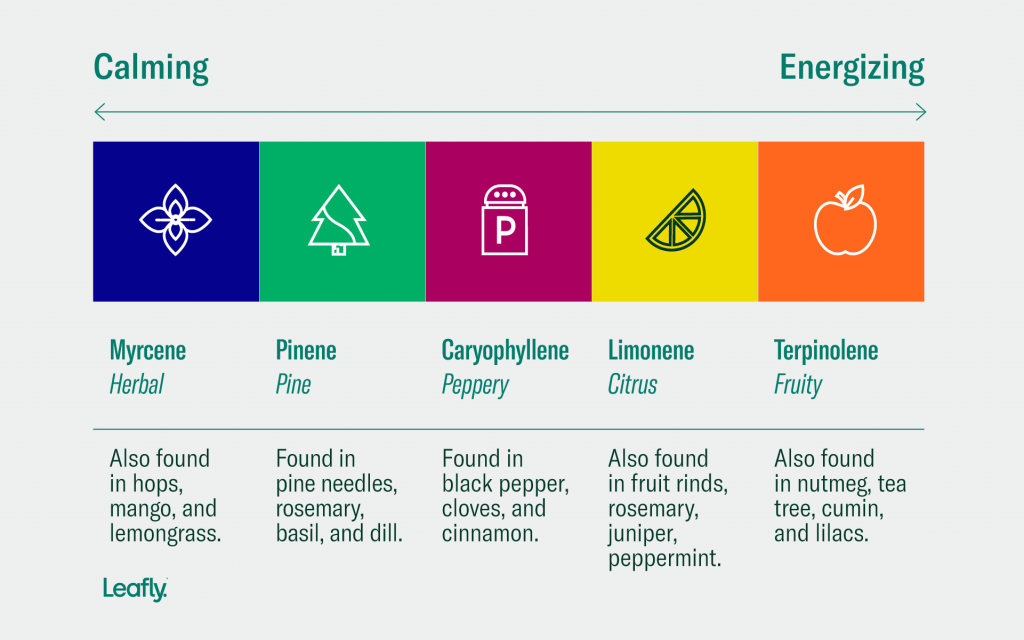
Terpenes
Secreted in the same glands that produce cannabinoids like THC and CBD, terpenes are aromatic oils that color cannabis varieties with distinctive flavors like citrus, berry, mint, and pine.
Over 100 different terpenes have been identified in the cannabis plant, and every strain tends toward a unique terpene type and composition. Each individual terpene is associated with unique effects; some promote relaxation and stress-relief, while others promote focus. At 253 Farmacy, we are always encouraging customers to get a good smell of our deli-style flower to determine which terpenes you enjoy.
Leafly has made some really great and useful infographics on the most popular terpenes. Check out their terpene guide…